


CARS/DGS evolved from the 1980 TR-1 Reconnaissance System [TRS] and the 1989 TR-1 Ground Station [TRIGS] programs, each designed to provide responsive airborne intelligence support for NATO. Originally, TRIGS was to be deployed in a bunker near Hahn, Germany, but in 1990 Congress directed an upgrade and redirection of the TRIGS system to support worldwide deployment.
Currently, it is composed of 27 transportable shelters and is capable of deployment to support operational requirements within 72 hours. Each shelter is ten by twenty-two feet and can be transported by air, sea or highway. The unit provides its own generators and power distribution equipment as well as environmental control units for system cooling. CARS may be set up on parking lots, packed gravel pads or settled earth. Space requirements for a full CARS deployment, allowing for spatial separation for the antenna farm, requires an area approximately the size of a football field.
The Contingency Airborne Reconnaissance System / Deployable Ground Station [CARS/DGS] is comprised of five segments:
The Mission Intelligence Segment [MIS] is responsible for mission control and imagery exploitation of Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar System [ASARS] data.The CARS PM develops transition plans then conducts integration testing. There are 7 different contractors, 7 different integration segments, 7 different PMs for the CARS. Edwards AFB approves all flight test plans. Warner Robins conducts flight testing. The Mission Intelligence Segment (MIS) exploitation segment of CARS is the same as JSIPS-A. Co-location of CARS and JSIPS-A, will save money by capitalizing on both systems' capabilities together instead of separately.The Deployable Ground Intercept Facility [DGIF-2] has 17 operator positions that can collect, analyze and report Signals Intelligence [SIGINT] data.
The Ground Control Processor-VIII [GPF-VIII] provide Electronic Intelligence [ELINT] data processing and reporting.
The Communications Segment [COS] provides a centralized demarcation point for all DGS external communications, including interfaces for either tactical, in-garrison, or commercial communications hookups. External data connectivity is provide through JWICS, SIPRNET, AUTODIN and TADIL-B. UHF and HF radios provide VPN, PRISM GOOSE, CTT and TDT access.
The Mobile Stretch [MOBSTR] is composed of two segments and two antennae in an easily deployable configuration. MOBSTR permits the DGS to remain in garrrison while supporting forward deployed aircraft. Using MOBSTR, data is downlinked from the airborne platform to the MOBSTR segment for processing. The data is then forwarded to the CONUS-based garrisoned DGS for exploitation.
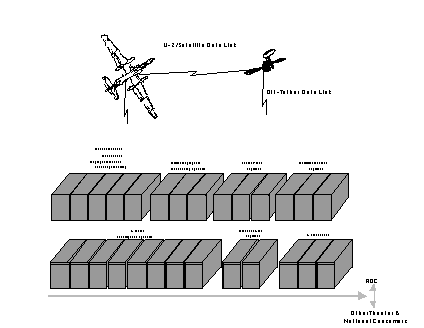
There are two U-2 Deployable Ground Segments. DGS I, which achived an initial operational capability on 01 November 1994, is permanently assigned to Langley AFB VA. DGS II achieved an initial operational capability on 01 July 1995 and is permanently assigned to Beale AFB CA. Both DGS I and II are deployable to support operational requirements.
