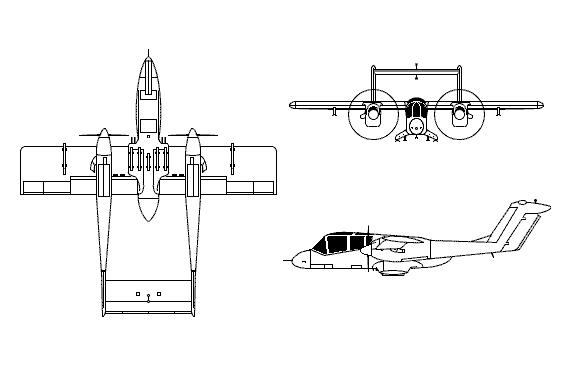








The OV-10 Bronco was a multi-purpose, light attack aircraft acquired by the Marine Corp for observation squadrons to conduct visual reconnaissance missions. The OV-10A is a twin-turboprop short takeoff and landing aircraft conceived by the Marine Corps and developed under an Air Force, Navy, and Marine Corps tri-service program. The first production OV-10A was ordered in 1966 and its initial flight took place in August 1967. The OV-10 can be used for short take-offs and landings on aircraft carriers without the use of catapults. With the second seat removed, it can carry 3,200 pounds of cargo, five paratroopers or two litter patients and an attendant.
The Bronco's mission capabilities include observation, forward air control, helicopter escort, armed reconnaissance, gunfire spotting, utility and limited ground attack; however, the USAF acquired the Bronco primarily as a forward air control (FAC) aircraft. The Bronco also provides transportation for aerial radiological reconnaissance, tactical air observers, artillery and naval gunfire spotting and airborne controllers of tactical air support operations. Other tasks include armed escort for helicopters and front line, low-level aerial photography.
The first USAF OV-10As destined for combat arrived in Vietnam on July 31, 1968. A total of 157 OV-10As were delivered to the USAF before production ended in April 1969.
Each of the Marine Corps' two observation squadrons had 18 aircraft, 9 OV-10As and 9 OV-10Ds night observation aircraft. There was also a Marine Air Reserve squadron. The OV-10 was phased out of the Marine Corps in 1995.
The OV-10 Night Observation Gunship (NOGS) was a USMC OV-10A modified to include a turreted FLIR sensor and turreted M-197 20-mm gun slaved to the FLIR aimpoint. Successful in combat in Vietnam, NOGS evolved into the NOS OV-10D, which included a laser designator.
Although the United States no longer flies the OV-10, other countries continue to operate the Bronco.






