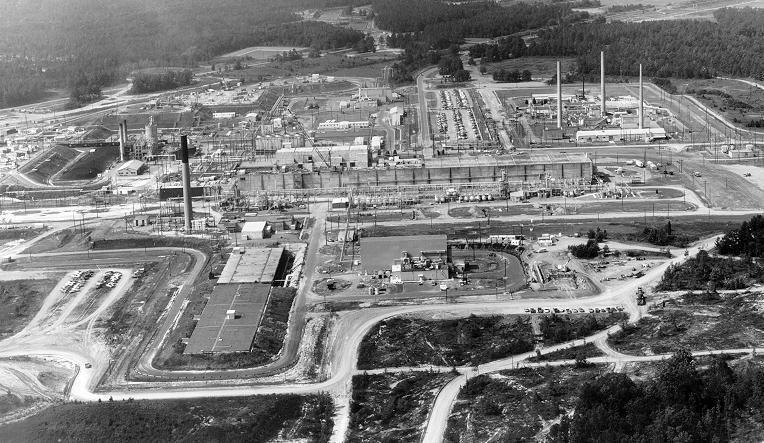


Canyon operations historically recovered uranium-235 (U-235), the fuel source for nuclear reactors, by a chemical separation process of reprocessing aluminum-based enriched-uranium fuel rods from site reactors and other test and research reactors to recover usable U-235 for recycle into new fuel elements. The recovered uranium was shipped as a liquid to the U.S. Department of Energy's Oak Ridge (Tennessee) site for reuse. In addition, the canyon was equipped with special capabilities to recover neptunium-237 (Np-237) and plutonium-238 (Pu-238) from the reactor fuel and special irradiated targets. Pu-238 is used in power systems for deep space exploration. Np-237 is used to produce Pu-238 by nuclear irradiation. Processing of spent fuels from SRS reactors was interrupted in 1988 due to a decision to halt liquid uranium shipments. In July 1996 DOE determined that H Canyon should be used to convert a large quantity of weapons-usable HEU to low-enriched material, no longer weapons-usable, but suitable as fuel in commercial power reactors.
The 200-H area also includes the Tritium Processing Buildings, Receiving Basins for Offsite Fuels {RBOF], and the Resin Regeneration Facility [RRF].
